Recently I bought an iPad so I can live share my notes to my laptop during screencasts. This is incredibly useful for online meetings, presentations, or pair programming sessions where I want to show notes to whoever in real-time.
In this blog post, I'll explain how I setup screen mirroring from my iPad to a NixOS based setup. Whether you are using NixOS as your daily driver or just want to try out screen mirroring on a *nix based system, hopefully my experience and learnings can be helpful for you.
Prerequisites
- An iPad with screen mirroring capabilities.
- A laptop or desktop computer running NixOS.
- Both devices connected to the same local network
Note that for the rest of this tutorial I'm running NixOS 22.11 (Raccoon) and an iPad (6th gen) running iOS 16.2.
Setting up an AirPlay receiver on NixOS
Apple devices canonically talk to each other via AirPlay, so in order to mirror an iPad to NixOS, we need to setup an AirPlay "receiver" server.
There are many open source AirPlay receivers, but I chose to use UxPlay simply
because it was the first one I came across and it's in nixpkgs.
Now unfortunately if we start running the receiver via nix run
nixpkgs#uxplay, the iPad won't see anything 😓. This is expected though
because the receiver has no way of interacting with the service discover
mechanism of AirPlay which is mDNS.
The UxPlay README recommends using Avahi for doing mDNS. Luckily Avahi is
available for NixOS so we can add it too our configuration.nix as follows:
1services.avahi = {2 nssmdns = true;3 enable = true;4 publish = {5 enable = true;6 userServices = true;7 domain = true;8 };9};
Now after a nixos-rebuild switch we should be running Avahi
1$ systemctl status avahi-daemon.service2* avahi-daemon.service - Avahi mDNS/DNS-SD Stack3 Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/avahi-daemon.service; enabled; preset: enabled)4 Active: active (running) since Tue 2022-12-27 09:12:57 EST; 13s ago5TriggeredBy: * avahi-daemon.socket6 Main PID: 245105 (avahi-daemon)7 Status: "Server startup complete."8 IP: 8.8K in, 8.8K out9 IO: 0B read, 0B written10 Tasks: 1 (limit: 38114)11 Memory: 628.0K12 CPU: 22ms13 CGroup: /system.slice/avahi-daemon.service14 `-245105 "avahi-daemon: running [spam.local]"1516Dec 27 09:12:57 spam avahi-daemon[245105]: New relevant interface lo.IPv4 for mDNS.17Dec 27 09:12:57 spam avahi-daemon[245105]: Network interface enumeration completed.18...
Now if we try running UxPlay again, we should see our AirPlay receiver show up in the screen mirror.
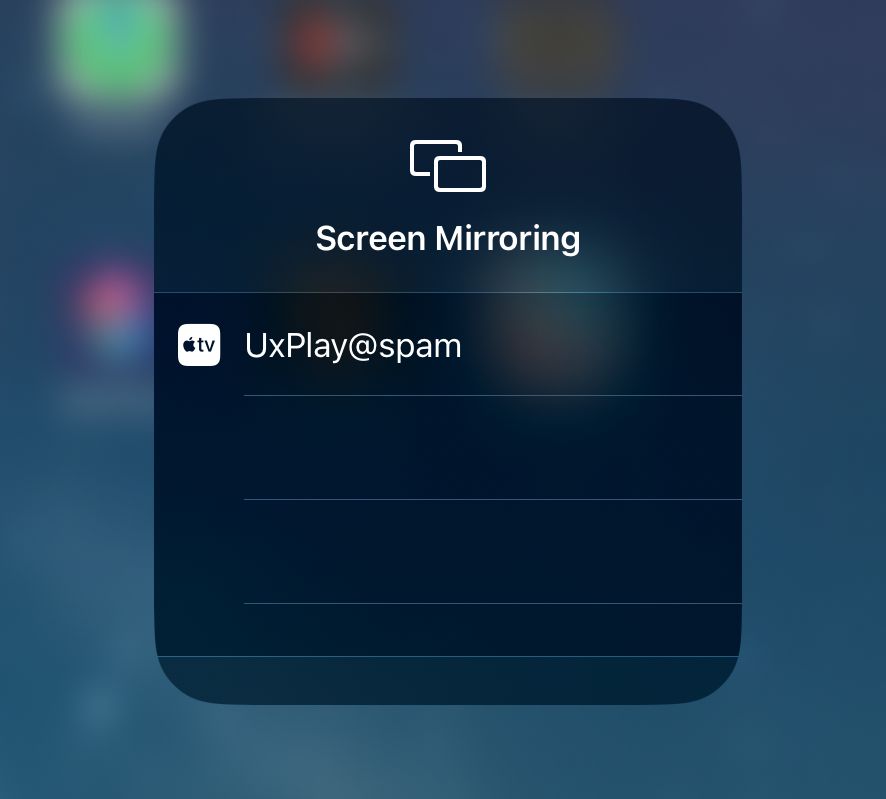 my iPad seeing UxPlay!
my iPad seeing UxPlay!
This is great! However if we try to connect we will just end up with a timeout. What gives?
After breaking out Wireshark it was obvious that is was a firewall issue. The
simple remedy to this problem was to set networking.firewall.enable = false;
in the configuration.nix. But this is in general a bad idea and should be
avoided.
Instead I went with a uxplay + iptables + bash approach so while the uxplay is running, iptables will allow incoming traffic to all necessary ports, and on exit, will close them again.
1#! /usr/bin/env nix-shell2#! nix-shell --quiet -p uxplay -i bash34set -ueo pipefail56## Clear any existing "DROP ME" rules7## ref: https://stackoverflow.com/a/63855690/123934228while sudo iptables -L -n --line-number | grep "DROP ME" > /dev/null; do9 sudo iptables -D INPUT $(sudo iptables -L -n --line-number | grep "DROP ME" | head -1 | awk '{print $1}');10done111213LOCAL_CIDR=${1:-"192.168.0.0/16"}1415open-port-tcp() {16 local port=$117 echo "Opening tcp port $port from $LOCAL_CIDR ..."18 sudo iptables \19 -I INPUT \20 -p tcp \21 -s $LOCAL_CIDR \22 --dport $port \23 -j ACCEPT \24 -m comment --comment "DROP ME"25}2627close-port-tcp() {28 local port=${1:-0}29 echo "Closing tcp port $port from $LOCAL_CIDR ..."30 sudo iptables \31 -D INPUT \32 -p tcp \33 -s $LOCAL_CIDR \34 --dport $port \35 -j ACCEPT \36 -m comment --comment "DROP ME"37}3839open-port-udp() {40 local port=$141 echo "Opening udp port $port from $LOCAL_CIDR ..."42 sudo iptables \43 -I INPUT \44 -p udp \45 -s $LOCAL_CIDR \46 --dport $port \47 -j ACCEPT \48 -m comment --comment "DROP ME"49}5051close-port-udp() {52 local port=${1:-0}53 echo "Closing udp port $port from $LOCAL_CIDR ..."54 sudo iptables \55 -D INPUT \56 -p udp \57 -s $LOCAL_CIDR \58 --dport $port \59 -j ACCEPT \60 -m comment --comment "DROP ME"61}6263open-port-tcp 710064open-port-tcp 700065open-port-tcp 700166open-port-udp 600067open-port-udp 600168open-port-udp 70116970# Ensure port closes if error occurs.71trap "close-port-tcp 7100 && \72 close-port-tcp 7000 && \73 close-port-tcp 7001 && \74 close-port-udp 6000 && \75 close-port-udp 6001 && \76 close-port-udp 701177 " EXIT7879uxplay -p
1$ ipad_screen_mirror_server2Opening tcp port 7100 from 192.168.0.0/16 ...3Opening tcp port 7000 from 192.168.0.0/16 ...4Opening tcp port 7001 from 192.168.0.0/16 ...5Opening udp port 6000 from 192.168.0.0/16 ...6Opening udp port 6001 from 192.168.0.0/16 ...7Opening udp port 7011 from 192.168.0.0/16 ...8using network ports UDP 7011 6001 6000 TCP 7100 7000 70019using system MAC address xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx10Initialized server socket(s)
Here is the gist for those interested.
Now wrapping all this code into a simple script gives us an easy way to easily spin up an AirPlay receiver server!
If you want to learn more about screen mirroring or NixOS, here are some additional resources you might find helpful:
- NixOS documentation (https://nixos.org/manual/)
- mDNS RFC (https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/rfc6762.html)
- Publish a service with Avahi on NixOS (https://blog.stigok.com/2019/12/09/nixos-avahi-publish-service.html)
- OpenAirPlay Spec (https://openairplay.github.io/airplay-spec/introduction.html)
I hope you found this useful, let me know if you have any other tips or tricks for screen mirroring on NixOS!
(ง ͠° ͟ل͜ ͡°)ง